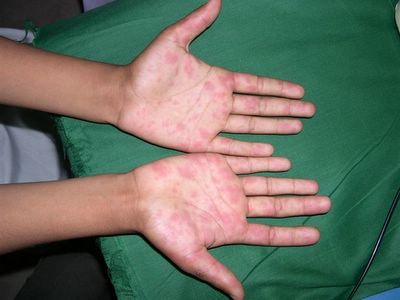
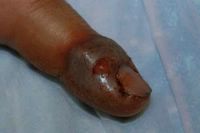
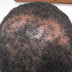
The patient accompanied her "mother" to the office. She is a 12 yo chihuaha with autoimmune thyroid disease and extensive alopecia areata. I was aksed what could be done and injected large areas of her skin with intralesional triamcinalone. Unfortunately, there is no billing code for this - the dog lacked health insurance.
(Actually, I deferred treatment until I hear from my august colleagues)
Note tail alopecia in Fig. 3

Fig 1
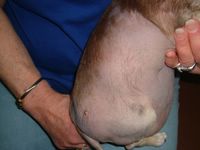
Fig 2
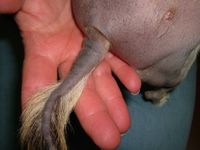
Fig. 3
Ref:
A natural canine homologue of alopecia areata in humans.
Tobin DJ, Gardner SH, Luther PB, Dunston SM, Lindsey NJ, Olivry T.
Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Bradford, Bradford, UK.
Br J Dermatol. 2003 Nov;149(5):938-50.
BACKGROUND: Alopecia areata (AA) is suspected to be an autoimmune disease directed preferentially against hair follicles (HF) affecting both humans and various mammalian species. Recently, two rodent models of AA were described, namely the ageing C3H/HeJ mouse and the DEBR rat. Despite several case reports of canine AA in the literature, there has been no systematic assessment of the disease in these companion animals, and it is also not known whether dogs with AA could be useful as an outbred homologue of this disease in humans. OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the clinical, histopathological and immunopathological features of 25 dogs with AA and compare these data with those found in the human disease. PATIENTS/METHODS: Twenty-five client-owned dogs exhibiting macroscopic alopecia with peri- or intrabulbar lymphocytic infiltrates were selected for study. Biopsies and sera were obtained and assessed by histopathology, direct immunofluorescence of immunoreactant deposition, immunohistochemistry for lymphocyte markers, indirect immunofluorescence and immunoblotting analysis of circulating serum IgG, selective immunoprecipitation of HF proteins by serum IgG, and passive transfer of purified canine IgG into naive C57BL/10 mice. RESULTS: Clinical signs including alopecia, skin hyperpigmentation and leucotrichia usually developed during adulthood and were first seen on the face, followed by the forehead, ears and legs. Spontaneous remission of alopecia occurred in 60% of dogs and regrowing hair shafts were often non-pigmented. Histological examination of skin biopsy specimens revealed peri- and intrabulbar mononuclear cell infiltrates affecting almost exclusively anagen HF. Direct immunofluorescence analysis detected HF-specific IgG in 73% of dogs, while indirect immunofluorescence revealed circulating IgG autoantibodies to the HF inner and outer root sheaths, matrix and precortex. Immunoblotting analysis revealed IgG reactivity to proteins in the 45-60 kDa molecular weight range and with a 200-220 kDa doublet. The latter was identified as trichohyalin by selective immunoprecipitation. Purified HF-reactive IgG, pooled from AA-affected dogs, was injected intradermally to the anagen skin of naive mice where it was associated with the local retention of HFs in an extended telogen phase in AA-treated skin compared with that seen in controls. CONCLUSIONS: These findings are very similar to those reported for human AA patients; therefore, they support the consideration of dogs with AA as a useful homologue for the study of the pathogenesis of this common autoimmune disease of humans.
(Actually, I deferred treatment until I hear from my august colleagues)
Note tail alopecia in Fig. 3

Fig 1

Fig 2

Fig. 3
Ref:
A natural canine homologue of alopecia areata in humans.
Tobin DJ, Gardner SH, Luther PB, Dunston SM, Lindsey NJ, Olivry T.
Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Bradford, Bradford, UK.
Br J Dermatol. 2003 Nov;149(5):938-50.
BACKGROUND: Alopecia areata (AA) is suspected to be an autoimmune disease directed preferentially against hair follicles (HF) affecting both humans and various mammalian species. Recently, two rodent models of AA were described, namely the ageing C3H/HeJ mouse and the DEBR rat. Despite several case reports of canine AA in the literature, there has been no systematic assessment of the disease in these companion animals, and it is also not known whether dogs with AA could be useful as an outbred homologue of this disease in humans. OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the clinical, histopathological and immunopathological features of 25 dogs with AA and compare these data with those found in the human disease. PATIENTS/METHODS: Twenty-five client-owned dogs exhibiting macroscopic alopecia with peri- or intrabulbar lymphocytic infiltrates were selected for study. Biopsies and sera were obtained and assessed by histopathology, direct immunofluorescence of immunoreactant deposition, immunohistochemistry for lymphocyte markers, indirect immunofluorescence and immunoblotting analysis of circulating serum IgG, selective immunoprecipitation of HF proteins by serum IgG, and passive transfer of purified canine IgG into naive C57BL/10 mice. RESULTS: Clinical signs including alopecia, skin hyperpigmentation and leucotrichia usually developed during adulthood and were first seen on the face, followed by the forehead, ears and legs. Spontaneous remission of alopecia occurred in 60% of dogs and regrowing hair shafts were often non-pigmented. Histological examination of skin biopsy specimens revealed peri- and intrabulbar mononuclear cell infiltrates affecting almost exclusively anagen HF. Direct immunofluorescence analysis detected HF-specific IgG in 73% of dogs, while indirect immunofluorescence revealed circulating IgG autoantibodies to the HF inner and outer root sheaths, matrix and precortex. Immunoblotting analysis revealed IgG reactivity to proteins in the 45-60 kDa molecular weight range and with a 200-220 kDa doublet. The latter was identified as trichohyalin by selective immunoprecipitation. Purified HF-reactive IgG, pooled from AA-affected dogs, was injected intradermally to the anagen skin of naive mice where it was associated with the local retention of HFs in an extended telogen phase in AA-treated skin compared with that seen in controls. CONCLUSIONS: These findings are very similar to those reported for human AA patients; therefore, they support the consideration of dogs with AA as a useful homologue for the study of the pathogenesis of this common autoimmune disease of humans.